Valleys of the Dammed

© mqrphoto
- Why is China building so many large dams on the Tibetan plateau?
- The large dams in Tibet—who are they for?
- Are extensive impact assessments carried out by Chinese engineers before building of new dams?
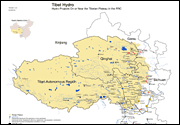
- In potential planning stages is a dam in Tibet twice the size of the Three Gorges Dam. Where?
- There is a dam under way in Sichuan that is as tall as the Eiffel Tower. What is the name of that dam?
- Are there alternatives to dams for providing energy in Tibet?
- In southwest China, Chinese environmental groups are rallying fiercely to prevent construction of large new dams. Have these groups been successful with this goal?
- Why does China have more big dams within its borders than the rest of the world combined?
- What is the largest concrete object on earth?
- What is the tallest arch dam on earth? Answer here
DAMMING the HECK out of the RIVERS of TIBET
...seems to be the Chinese plan to achieve Carbon Neutrality by 2060. Over 60 percent of China's energy currently comes from coal, the dirtiest source of energy consumption on the planet. In September 2020, the biggest Fossil Fool of all time, Xi Jinping, announced at a UN video conference that China would achieve carbon neutrality by 2060. Xi Jinping did not show up at the UN in person to deliver this important speech, because he appears to be terrified of catching a virus called Covid-19. Nor did he show up at COP26 in Glasgow, snubbing all the world leaders gathered there—and dodging the bullet on responsibility for China's whopping 28 percent output of annual global CO2.
Xi Jinping is full of great green words offering wonderful promises—but he declined to say exactly how China, a nation of 1.4 billion, would ease off on its heavy coal addiction and make the transition to renewable sustainable energy. But the August 2021 issue of China Report ASEAN Magazine gives some clues. The magazine is made in Beijing and distributed in Asia. The theme of this issue is: Creating a Cargon-free Future.
A feature in the magazine reveals that by 2060, electricity demand is China is expected to DOUBLE from 2019 figures, even though the population will remain steady at 1.4 billion. To cater to this mega amount of electricity demand, the feature says that renewable electricity demand would be ramped up by a 16-fold increase in solar, 9-fold increase in wind power, six-fold increase in nuclear energy. Which all sounds admirable, until we arrive at the next figure: hydropower needs to double from 2019 output. Consider this: China has more large dams than the rest of the world COMBINED. Last time I checked, that was 26,000 large dams in China—and that is an old figure. And China wants to DOUBLE the hydropower output by 2060? That is utter insanity.
For one thing, all China's existing megadams will be 40 years older by 2060. That means they will be falling apart. They either need to be rebuilt or taken down and replaced. And by 2060, with glaciers receding, there may not be river power to drive the gigantic turbines in these megadams.
To double the amount of hydropower in China by 2060, there is only one place where such energy can be sourced: Tibet. Already, Chinese planners are talking about a mega mega dam or a series of dams at the Great Bend of the Yarlung Tsangpo in eastern Tibet, which in combination with other dams in a cascade on the river might generate 70 GW of power. At the expense of destroying this mighty river and the ecosystems that depend on it. Megadams are no way a climate mitigation solution. This is false. This is the Green Dam Myth. Dams destroy rivers.
Megadams are neither renewable or sustainable. Their gigantic reservoirs give off methane emissions from rotting flooded vegetation. Methane is 30 times more potent as a greenhouse gas than CO2. So there goes the clean and green angle. Dams are dirty, and they are built in China with corrupt money, with contracts going out to corrupt officials.
BIG dams, BIG problems

Zipingpu Dam, Min River (Yangtse tributary), Sichuan
Capacity 760 MW, wall-height 158 metres
GE Coordinates: 31 02 10 N, 103 34 27 E
Zipingpu Dam has been implicated in the great Sichuan earthquake which killed over 80,000 people and left 5,000,000 homeless. Despite warnings by Chinese geologists, the hydropower company built the dam, with its massive reservoir lying directly on a major fault. The weight of the reservoir may have either triggered the earthquake or may have magnified what would have been a minor earthquake.

Pubugou Dam, Dadu River (Yangtse tributary), Sichuan
Capacity 3600 MW, wall-height 186 metres
GE Coordinates: 29 12 20 N, 102 50 20 E
At this site, local residents held some of the largest protests against dam construction in China. In late 2004, as work commenced on the dam, the construction site was overrun by thousands of farmers (a crowd estimated to be 10,000 strong), incensed about evictions stemming from planned flooding of the region. Thousands of protesters were jailed, and some killed. Local government officials were convicted of corruption. Dam construction was delayed by a year. Violence flared up again in early 2010 when farmers were forcibly evicted from their homes to make way for reservoir flooding. In all, around 100,000 people were displaced by the project. The dam reservoir has destroyed some of the best farmland in China.
WHAT IS A LARGE DAM?
A large dam is defined as over 15 metres in height (wall height from the base up), or with a reservoir containing 3 million cubic metres of water or more. There is no firm definition of a 'mega-dam', but roughly ten times bigger than a large dam would seem to qualify, with a benchmark of around 150 metres in wall height. And then, on this website, references are made to the MONSTER dam, roughly 250 metres or more in wall height. Monster dams rank among the world's biggest (width or height or both).
In a class all of its own is the Three Gorges Dam, starting up on the mid-reaches of the Yangtse in 2009. The Three Gorges Dam has a wall-height of 180 metres, is over 2 kilometres wide, and has a generating capacity of 22.5GW (gigawatts) or 22,500 MW (megawatts). The 600-kilometre-long reservoir at the Three Gorges Dam reached full height in 2010, submerging 13 cities, 140 towns and 1,350 villages. This dam, which has displaced up to two million people, is the biggest dam in the Motherland, or the Mother of all Dams. Its environmental impact is uncertain.
China is building dams like there's no tomorrow—it is far and away the world's first builder of large dams. There are estimated to be over 50,000 large dams worldwide. Here's an astonishing statistic: almost half that number of large dams is situated within the borders of China—over 23,000 large dams are under operation in China today. Another astonishing statistic: there are at least 11,000 more large dams in South Asia—including over 4,500 large dams in India. That brings the total of large dams in China/South Asia to over 34,000, which means roughly 70 percent of the world's large dams are situated in China and South Asia. This does not bode well for the rivers of this region.
In the Himalayan region, although there are clear and urgent signs of imminent threat from climate change in the form of rapidly melting glaciers, both China and India are forging ahead with building of large dams. Both nations appear to be oblivious of the climate change threat—neither is adopting a more cautious approach to dam building in the Himalayan region. It does not make sense to build scores of large dams in a stark future where there may be no flow of water anyway—due to major rivers drying up.
China exports its mega-dam engineering expertise and financial backing to impoverished nations in Asia, Africa and elsewhere—initiating projects with very little impact assessment, if any. These projects are potentially devastating to indigenous people, who are rarely consulted about the projects. Mega-dams can potentially trigger ecological havoc on a huge scale. For more on Environmental Impact Assessments (or the lack of them) go to Secret Dam Construction.
WHAT'S THE DAM-AGE?
World's Top Four Builders of Large Dams | |
| China | 22,000 large dams |
| USA | 6,575 |
| India | 4,291 |
| Japan | 2,675 |
Note: source is the World Commission on Dams, circa 2003, which means these figures are not current. Add a few thousand large dams in the case of China to bring the number up to date.
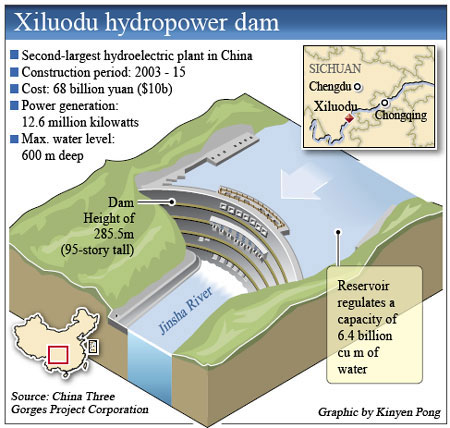
Xiluodu Dam on Yangtse
monster dams
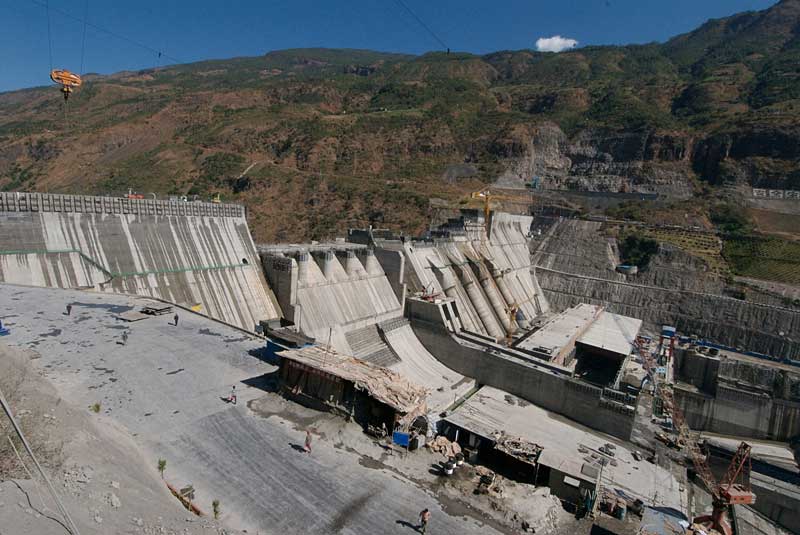
There are big dams, and then there are mega-dams. Sichuan and Yunnan provinces in southwest China are home to the MONSTER dam. Under construction are dams with wall heights approaching 300 metres—close to the height of a 95-storey building.
Xiluodu Dam, straddling the Yunnan-Sichuan border on the Jinsha River (upper Yangtse) is coming online. This concrete colossus stands around 280 metres tall, and has a generating capacity of 12.6GW by one estimate, and 13.8GW by another estimate. Xiluodu is the second-biggest dam in China after the Three Gorges Dam, and constructed by the same company, Three Gorges Project Corporation. Not far off, the third-biggest dam in the world, Xiangjiaba, is under way—projected for completion in 2014, with a generating capacity of 6.4GW. Together, Xiluodu and Xiangjiaba would generate 20GW (gigawatts) of energy—enough to power all the homes in England. Both dams have been constructed by the Three Gorges Project Corporation, which is involved in a cascade of dams on this river. These include two more monster dams, Beihaitan (capacity 12.6GW, wall-height 277m) and Wudongde (capacity 7.4GW, wall height 235m)—both projected for completion by 2020.
What does all this mean for the Jinsha (upper Yangtse) River? Death by dams, basically. Liu Jianqing, an environmental journalist and campaigner puts it this way:

“[The Jinsha] is big and beautiful. But if you have 25 dams and every 100 kilometres there is a dam, then you don't have a river. You will never have a river again. It means you won't have fish, you will lose a lot of land and many people have to lose their homes. We call that a dead river.”
People are incensed about losing homes and valuable farmland because of the dams. There have been outbreaks of unrest along the Jinsha. In 2011, riot police quelled a "mass disturbance" in Suijiang town, where 60,000 people are being forcibly relocated to make way for Xiangjiaba Dam.
Huge dams like this have the potential for creating environmental chaos—by disrupting fish migration and sediment flow, reducing biodiversity, and by degrading water quality. The huge dam itself poses a significant safety hazard as the structure ages. The resulting reservoir displaces entire communities, floods and fragments ecosystems, increases water-borne diseases, and could trigger earthquakes.
During the building of the Three Gorges Dam, over two million people had to be relocated because of the constant threat of landslides (a group of hydraulic engineers reported that over 4,700 landslides had taken place in the vicinity by March 2007). Construction of the Three Gorges, Xiluodu and Xiangjiaba dams on the Yangtse have been plagued by corruption, technical problems, human rights problems and profound environmental impact.